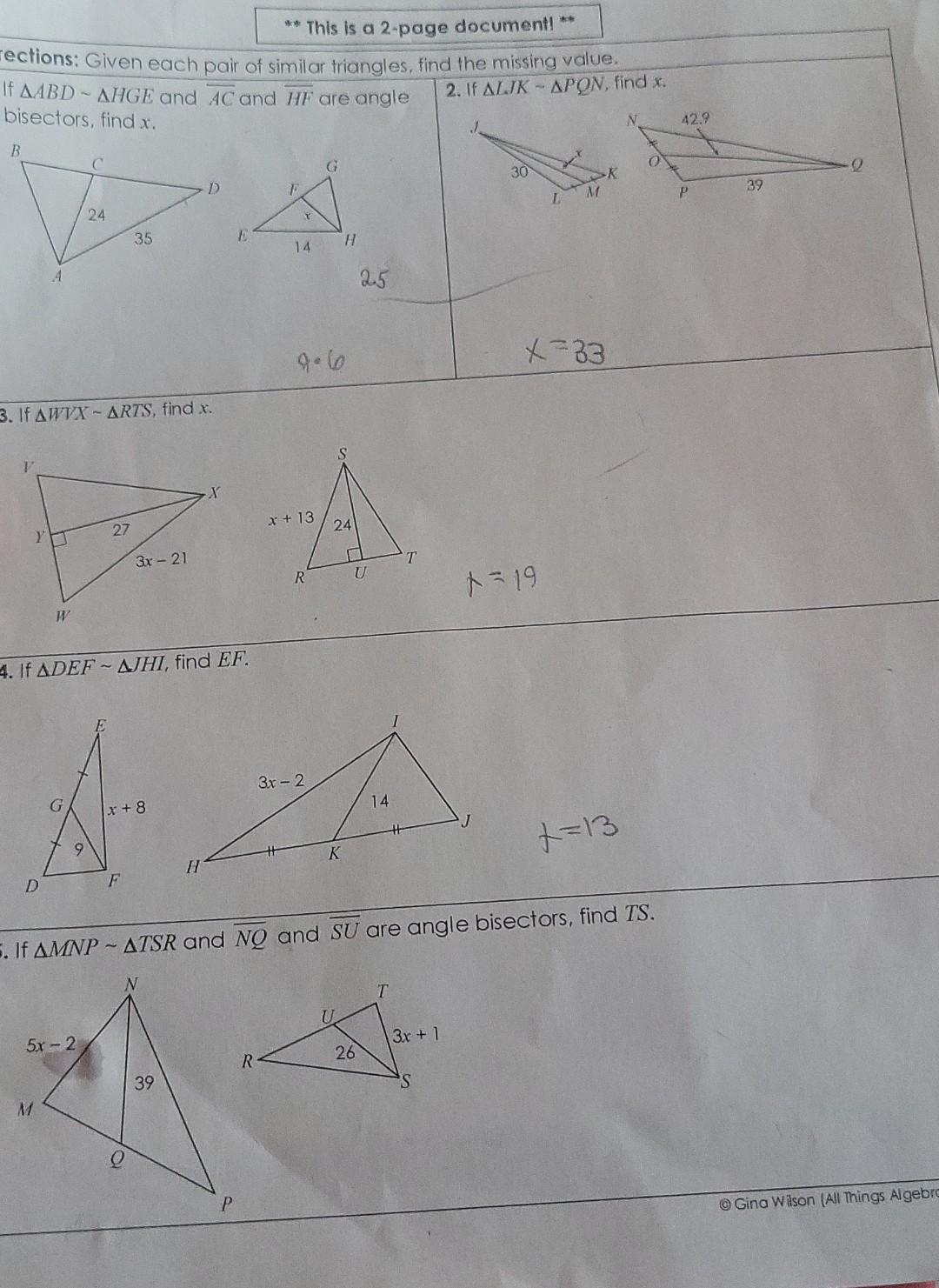
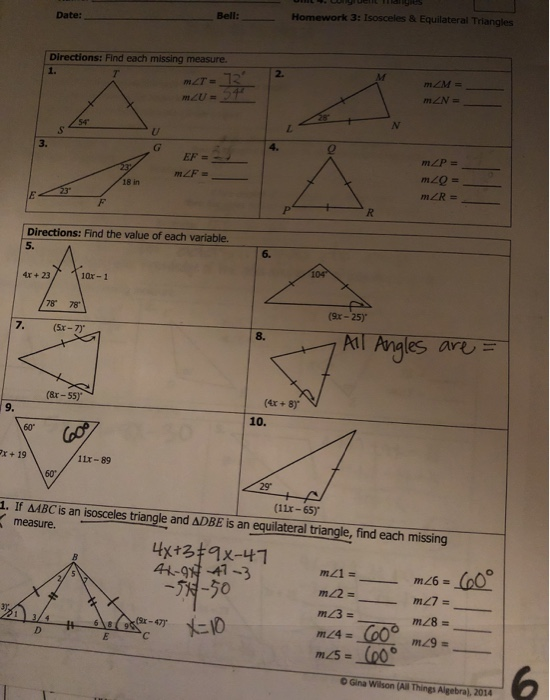
Geometry enthusiasts and students alike often find themselves diving deep into the world of similar triangles, a fascinating area of study in mathematics. In this article, we will explore the answers to Unit 6 Similar Triangles Homework 3, providing you with step-by-step explanations, essential formulas, and practical examples. Whether you're a student struggling with geometry or simply curious about similar triangles, this guide is for you.
Understanding the concept of similar triangles is crucial as it lays the foundation for more advanced topics in geometry and trigonometry. By the end of this article, you'll not only have the answers to your homework but also a deeper understanding of how similar triangles work in real-world applications.
We will cover various aspects of similar triangles, including their properties, how to identify them, and the methods to solve problems related to them. So, let's dive right in and unravel the mysteries of Unit 6 Similar Triangles Homework 3 answers.
Read also:Marivi Lorido Garcia A Comprehensive Guide To Her Life Career And Achievements
Here's a quick table of contents to help you navigate through this article:
Introduction to Similar Triangles
Similar triangles are triangles that have the same shape but not necessarily the same size. This means that their corresponding angles are equal, and their corresponding sides are proportional. Understanding the concept of similar triangles is vital because it helps in solving various geometric problems, from calculating heights of tall objects to determining distances in maps.
In Unit 6, students are introduced to the properties and applications of similar triangles. Homework 3 specifically focuses on applying these properties to solve real-world problems. By mastering this unit, students can enhance their problem-solving skills and develop a deeper appreciation for geometry.
Properties of Similar Triangles
Angle-Angle Criterion
One of the primary ways to determine if two triangles are similar is by using the Angle-Angle (AA) criterion. If two angles of one triangle are congruent to two angles of another triangle, then the triangles are similar. This property is incredibly useful in proving similarity without needing to measure all sides.
Side-Side-Side Similarity
Another method to establish similarity is through the Side-Side-Side (SSS) criterion. If the ratios of the corresponding sides of two triangles are equal, then the triangles are similar. For example, if Triangle ABC has sides measuring 3, 4, and 5, and Triangle DEF has sides measuring 6, 8, and 10, the two triangles are similar because the ratios of their corresponding sides are equal (2:1).
Methods to Solve Unit 6 Homework 3
Solving Unit 6 Similar Triangles Homework 3 involves a combination of theoretical knowledge and practical application. Here are some methods to approach the problems:
Read also:What Was The Skin Disease That Michael Jackson Had Unveiling The Truth
- Identify the given information: Begin by listing all the known values, such as angles and side lengths.
- Apply similarity criteria: Use the AA, SSS, or SAS (Side-Angle-Side) criteria to determine if the triangles are similar.
- Set up proportions: Once similarity is established, use proportions to calculate unknown values.
For instance, if you are given two triangles with two pairs of congruent angles, you can immediately conclude that the triangles are similar using the AA criterion. From there, you can calculate missing side lengths using the ratio of corresponding sides.
Common Problems and Solutions
Problem 1: Identifying Similar Triangles
One common problem in Unit 6 Homework 3 is identifying whether two triangles are similar. Here's how you can approach this:
- Check if two angles of one triangle are congruent to two angles of the other triangle (AA criterion).
- Alternatively, check if the ratios of the corresponding sides are equal (SSS criterion).
For example, consider two triangles: Triangle ABC with angles 30°, 60°, and 90°, and Triangle DEF with angles 30°, 60°, and 90°. Since the angles are congruent, the triangles are similar.
Problem 2: Calculating Missing Side Lengths
Another frequent problem involves calculating missing side lengths. To solve this, use the property of proportionality:
Let's say Triangle ABC is similar to Triangle DEF, and you know the following:
- AB = 6, BC = 8, and AC = 10
- DE = 3, EF = x, and DF = 5
Using the proportionality property:
AB/DE = BC/EF = AC/DF
Substituting the known values:
6/3 = 8/x = 10/5
Solving for x:
8/x = 2
x = 4
Therefore, EF = 4.
Real-World Applications
Similar triangles have numerous real-world applications. Architects use them to design buildings and calculate dimensions. Engineers apply similar triangles to determine distances and heights in construction projects. Even photographers use the principles of similar triangles to achieve the perfect perspective in their shots.
For example, if you want to calculate the height of a tree without climbing it, you can use similar triangles. By measuring the shadow of the tree and comparing it to the shadow of an object of known height, you can determine the tree's height using proportions.
Tips for Students
Here are some tips to help students excel in Unit 6 Similar Triangles Homework 3:
- Practice regularly to improve your problem-solving skills.
- Memorize the similarity criteria (AA, SSS, SAS) and their applications.
- Use diagrams to visualize the problems and make solving them easier.
- Seek help from teachers or online resources if you're stuck.
Frequently Asked Questions
Here are some common questions students have about similar triangles:
- What is the difference between congruent and similar triangles? Congruent triangles are identical in shape and size, while similar triangles have the same shape but not necessarily the same size.
- How do I know if two triangles are similar? Use the AA, SSS, or SAS criteria to determine similarity.
- Can similar triangles have different orientations? Yes, similar triangles can be rotated or reflected, but they will still maintain their proportional relationships.
Conclusion
In conclusion, mastering Unit 6 Similar Triangles Homework 3 requires a solid understanding of the properties and applications of similar triangles. By applying the AA, SSS, or SAS criteria and using proportions, you can solve a wide range of geometric problems. This knowledge not only helps in academic success but also has practical applications in various fields.
We encourage you to practice regularly and explore real-world examples to deepen your understanding. Don't forget to leave a comment or share this article with your peers. For more resources on geometry and mathematics, explore our other articles on the site.